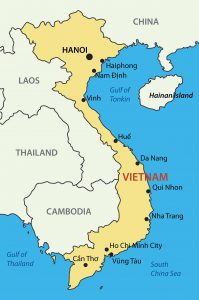
 Vietnam has a loosely shape of an “S” with a distance from north to south of 1650 km (1025 miles) and 50 km (31 miles) wide at the narrowest point of the “S”. According to Wikipedia.org, Vietnam is approximately 331,212 square kilometers (127,8812 square miles).
Vietnam has a loosely shape of an “S” with a distance from north to south of 1650 km (1025 miles) and 50 km (31 miles) wide at the narrowest point of the “S”. According to Wikipedia.org, Vietnam is approximately 331,212 square kilometers (127,8812 square miles).
To give us some visual reference on size and weather of Vietnam, I compared Vietnam to the United States. I found New Mexico closest in square kilometers or miles (121,598 miles). Central and southern California is almost similar to Northern Vietnam in weather except California is much dryer. Southern Florida is very similar to Vietnam in the humidity factor.
According to the Netstate.com and Worldometers.info, Vietnam is slightly smaller than California in size. California is approximately 423,999 square kilometers (163,707 square miles) with the distance from the north to south of 1674 kilometers (1040 miles) and the distance from east to west of 901 kilometers (560 miles.) However, Vietnam is much more densely populated than California. It has almost three times the people. California’s population in 2017 is estimated about 39.5 million while Vietnam is estimated to be about 95 million. Vietnam also has 3260 kilometers (2026 miles) of coastline and California has 1352 kilometers (840 miles) long of coastline. Vietnam is a great place for seafood lovers and beautiful beaches.
Bordering northern Vietnam is China. Laos is bordered to the north and central west while Cambodia is bordered to the southwest. The entire east side of Vietnam is coastline bordering the Gulf of Tonkin, South China Sea, and Gulf of Thailand.
The terrain of Vietnam is filled with tropical lowlands, hills, and densely forested highlands with less than 20% level land. That is probably one of the reasons why there is very little dairy such as milk and cheese in Vietnam. Because the lack of prairie flat land, cows are hard to raise. We see more water buffaloes which were used as tractors for farmland. No wonder I am lactose intolerant. I did not grow up with dairy products. For me the closest to drinking milk was powder milk or condense milk.
Vietnam is divided into four regions: the highlands and the Red River Delta in the north, the central mountains, the coastal lowlands, and the Mekong Delta in the south. Each of the region is rich in soil and natural resources. The rugged terrain and the flooded plains yield to the fertile rice paddy.
Tribal minority lives in the highlands in the north and northwest region. This region is also called Dãy Trường Sơn (Annamite Range). The terrain is rugged and narrow, nevertheless the soil is very fertile for rice and corn terrace farming.
The Red River Delta, also known as Sông Hồng, is smaller than the Mekong Delta but more densely populated. The Red River helps irrigate the rich rice-growing delta.
The central mountains, also called Tây Nguyên, has rugged mountain peaks, extensive forests, rich soil and natural resources. According to wikipedia.org, these central highlands are being served as areas for which people can relocate from the densely populated lowlands.
Coastal lowlands are narrow and flat extending from south of the Red River Delta to the Mekong River basin. Generally the coastal strip is fertile for rice cultivation.
The Mekong Delta is a low-level plain no more than three meters above sea level, criss-crossed by canals and rivers and three times larger in square kilometers than the Red River Delta. About 10,000 square kilometers of the delta is under rice cultivation. It is one of the major rice-growing regions of the world. The southern tip of Vietnam, known as the Cà Mau Peninsula is covered by dense jungle and mangrove.
The climate of the north, the central, and the south is slightly different from each other throughout the year. Vietnam has summer monsoon and receives nearly 90% of rainfall with high humidity during the summer months from May to October. The winter season extending from November to April in most parts of the country is dry or less rain. The average temperature is generally higher in the plains than the mountains. The temperature range from the low of 41 °F or 5 °C in December and January to more than 98.6 °F or 37 °C in August. The north can experience cold winter which can drop down to 50 °F or 10 °C. Central Vietnam can experience hot and dry winter while South Vietnam experience hot and humid throughout the year. Occasionally during the winter, snow may fall in the mountains with the highest elevation in the north in areas such as Sapa or Cao Sơn.
The rugged terrain with mountains jetted  irregularly in elevation and forms throughout the country yield a certain beauty and mystic to Vietnam. The monsoon season with high humidity contributes to spectacular water falls such as Bản Giốc Waterfall and blossoms plentiful of delicious tropical fruits such as rambuton (chôm chôm) or jackfruit (mít). Hạ Long Bay is only a small sample of northern Vietnam. Vietnam has so much to offer. I have been back to visit three times and there are still more to discover. I look forward to more adventure to come in the near future.
irregularly in elevation and forms throughout the country yield a certain beauty and mystic to Vietnam. The monsoon season with high humidity contributes to spectacular water falls such as Bản Giốc Waterfall and blossoms plentiful of delicious tropical fruits such as rambuton (chôm chôm) or jackfruit (mít). Hạ Long Bay is only a small sample of northern Vietnam. Vietnam has so much to offer. I have been back to visit three times and there are still more to discover. I look forward to more adventure to come in the near future.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geography_of_Vietnam
http://worldpopulationreview.com/states/california-population/
http://www.netstate.com/states/tables/st_size.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/California
http://www.worldometers.info/world-population/


